Incremental Generative Occlusion Adversarial Suppression Network for Person ReID
Cairong Zhao*
Xinbi Lv *
Shuguang Dou *
Shanshan Zhang, Member, IEEE
Jun Wu, Senior Member, IEEE
Liang Wang, Fellow, IEEE
(Cairong Zhao, Xinbi Lv, and Shuguang Dou contributed equally to this work.)
Abstract
Person re-identification (re-id) suffers from the significant challenge of occlusion, where an image contains occlusions and less discriminative pedestrian information. However, certain work consistently attempts to design complex modules to capture implicit information (including human pose landmarks, mask maps, and spatial information). The network, consequently, focuses on discriminative features learning on human nonoccluded body regions and realizes effective matching under spatial misalignment. Few studies have focused on data augmentation, given that existing single-based data augmentation methods bring limited performance improvement. To address the occlusion problem, we propose a novel Incremental Generative Occlusion Adversarial Suppression (IGOAS) network. It consists of 1) an incremental generative occlusion block, generating easy-to-hard occlusion data, that makes the network more robust to occlusion by gradually learning harder occlusion instead of hardest occlusion directly. And 2) a global-adversarial suppression (G&A) framework with a global branch and an adversarial suppression branch. The global branch extracts steady global features of the images. The adversarial suppression branch, embedded with two occlusion suppression module, minimizes the generated occlusion’s response and strengthens attentive feature representation on human non-occluded body regions. Finally, we get a more discriminative pedestrian feature descriptor by concatenating two branches’ features, which is robust to the occlusion problem. The experiments on the occluded dataset show the competitive performance of IGOAS. On Occluded-DukeMTMC, it achieves 60.1% Rank-1 accuracy and 49.4% mAP.
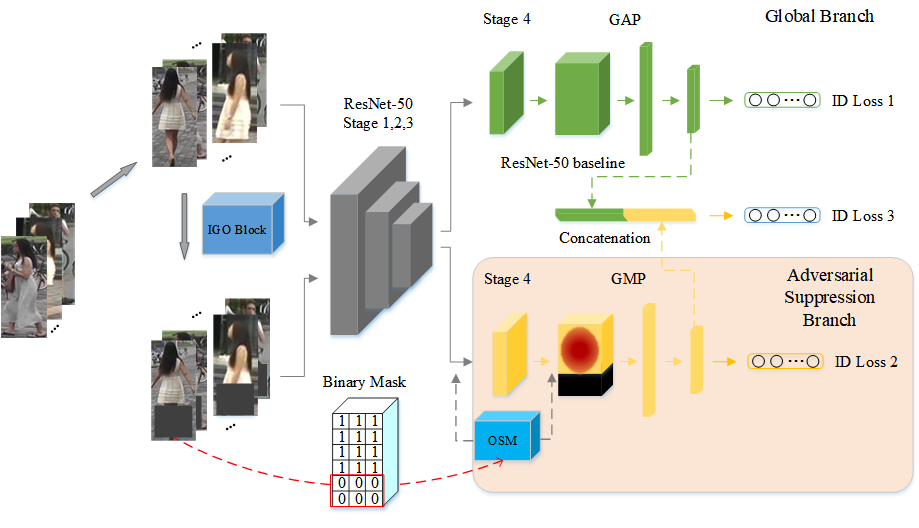
Figure 1.The flowchart of the proposed IGOAS network
Specifically, in the training phase, the IGO block converts the raw input into occluded data, and then the raw data and the occluded data are entered into the respective branch of the frame for feature extraction. In global branch, we retain the ResNet-50 baseline to extract steady global features of the raw data. In adversarial suppression branch, the OSM and a global max pooling operation are employing to force this branch to suppress the occlusion’s response and strengthen discriminative feature representation on non-occluded regions of the pedestrian. Finally, we get a more robust pedestrian feature descriptor by concatenating two branches’ features. And in the test phase, the incremental occlusion block won’t be performed.
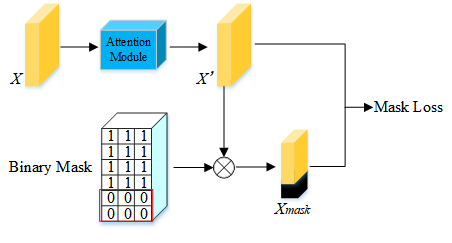
Figure 2.Structure of OSM
We propose an incremental generative occlusion adversarial suppression network. The IGOAS network first generates easy-to-hard occluded data through the IGO block and then suppresses the generated occluded region with the adversarial suppression branch. In this process of adversarial learning, the IGOAS learns a more discriminative and robust feature for the occlusion problem.
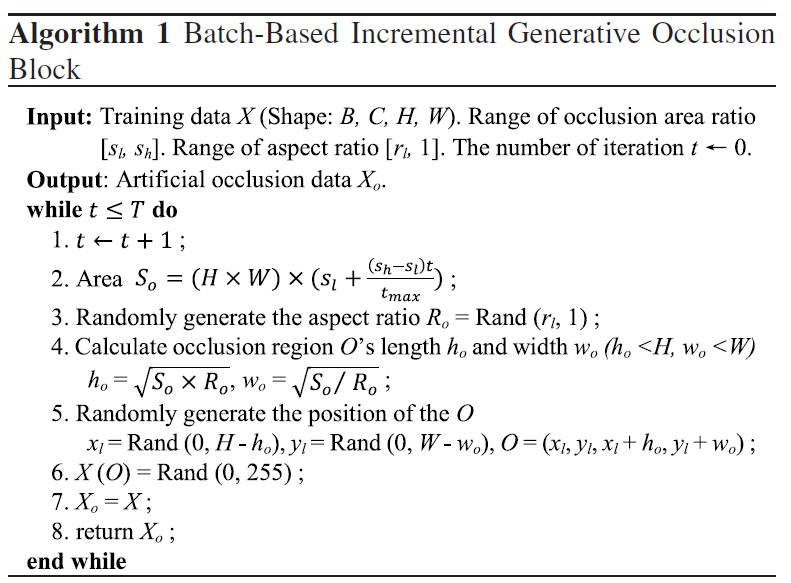
Figure 3.Batch-Based Incremental Generative Occlusion Block.
Paper
- Paper: PDF
Please consider citing if this work and/or the corresponding code are useful for you:
@article{tip21,
author = {Zhao, Cairong and Lv, Xinbi and Dou, Shuguang and Zhang, Shanshan and Wu, Jun and Wang, Liang},
title = {Incremental Generative Occlusion Adversarial Suppression Network for Person ReID},
journal = {IEEE transactions on image processing : a publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society},
volume = {30},
pages = {4212-4224},
DOI = {10.1109/tip.2021.3070182},
url = {<Go to ISI>://MEDLINE:33822724},
year = {2021},
type = {Journal Article}
}
Code
We use pytorch to implement igoas framework. Code is available online in ths github repository: https://github.com/Vill-Lab/IGOAS.